Advanced mud transport modelling
Study the impact of siltation on coastal morphology and water quality using this combined multi-fraction and multi-layer software
Why MIKE 21/3 Mud Transport?
Model the transport of mud and the interaction between mud and the bed
Analyse erosion, transport, settling and deposition of cohesive sediment in marine, brackish and freshwater areas taking fine-grained cohesive material into account. Perform the most comprehensive simulations that consider forcing by waves, salt-flocculation, the settling process, layered description of the bed, consolidation and morphological update of the bed.
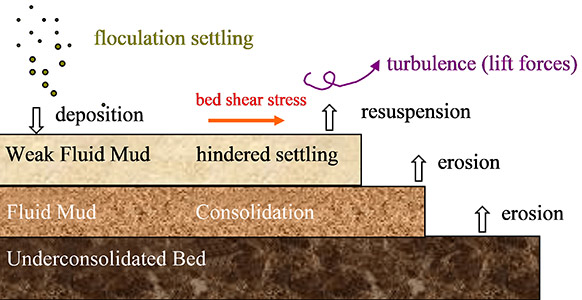
All of the physical processes modelled by MIKE 21/3 Mud Transport’s multi bed layer approach
Watch this simulation of sediment plume dispersion and the performance of the silt curtains carried out by Anse du Portier & Bouygues TP in Anse du Portier ‘s extension project.
Simulate all stages of the dredging process
Model suspended transport of fine grained non-cohesive sediment

Calculate both cohesive and non-cohesive sediment transport
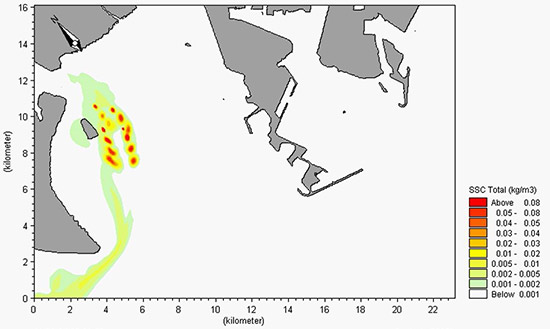
The introduction and development of dynamic sediment plumes in connection with reclamation and disposal operations in Singapore.
Estimate siltation rates to support port channel design and optimisation
Model bed load and mixed sediment transport
Near-bed transport in Ho Bay

Better assess the impact of a tailing dam break
For the most affordable access to these capabilities, check out our new Hydrodynamics subscription. Choose MT as your bonus module and take 40% off an annual subscription.
Gather key insight on siltation to advance your projects

Port Design
Investigate changes in sedimentation patterns and dredging requirements. Analyse the impact of siltation in harbours and access channels.

Dredging
Optimise dredging operations through comprehensive analyses of the spreading, dispersion and fate of dredged material.

Coastal Engineering
Study cohesive sediment dynamics and morphology such as erosion under combined waves and currents.

Water Quality
Understand the impact of contaminated sediments deposited in ecologically sensitive areas on local flora and fauna.
No in-house modellers?
DHI offers comprehensive modelling and consulting services to support impact assessments of cohesive sediments on coastal and estuarine environments.
Discover why customers count on MIKE 21/3 Mud Transport
Additional capabilities & unique features
The latest update introduces enhanced hotstart functionality, utilising layer and fraction distribution as initial conditions. Users now have additional options for erosion calculations, including a new RMS shear stress formulation and the ability to specify critical shear stress for each individual fraction. Dredging simulations benefit from new spilling types, expanding the scope of modelling possibilities. Furthermore, users can access new and improved outputs, such as extended output of mean velocity, bed distribution items, and three-dimensional bed parameters. To ensure optimal performance and accuracy, the update also includes substantial refactoring and modernization.
Save time and improve your modelling workflows using MIKE Zero’s upgraded editors and viewers. Take advantage of new keyboard shortcuts and themes, improved tabbing, tear off and cascade functionality plus easier access to User Guides and Scientific Documentation.
MIKE Zero, DHI’s fully Windows integrated graphical user interface, is now better than ever and comes standard with all MIKE 21/3 software. Enjoy easy access to new MIKE Cloud applications and Cloud-enhanced functionality, plus an extended set of MIKE tools within theme-based (rather than product-based) interactive workflows. Ensure important model components such as sources and structures stay at the forefront with a new interactive, customisable floating mapping window. Lastly, the updated tabbing functionality will help you work in a more organised and efficient manner.
Apply MIKE 21 Spectral Waves to calculate the influence of waves on erosion deposition patterns.
Point sources of dissolved and/or suspended components are important in many applications such as the release of sediments from rivers, intakes and outlets from cooling water or desalination plants. With MIKE 21/3 Mud Transport, you can specify source concentrations individually as either specified concentration or excess concentration.
If the morphological changes within the area of interest are expected to be comparable to the water depth in certain areas, this software can take the morphological impact on the hydrodynamics into consideration. Typical areas where this is necessary are shallow areas where long term effects are being considered or dredging/dumping sites in shallow areas.
If several bed layers are used, a transition rate can be applied. This will cause sediment from the top layers to be transferred to the subsequently lower layers.
MIKE 21/3 Mud Transport takes advantage of the efficient parallelisation techniques implemented in MIKE 21 for the use of multiple cores and GPUs. Special techniques have also been developed to enhance calculation speed within the morphological modelling.
The Mud Transport module is based on a multi-bed layered approach where each layer is described by a critical shear stress for erosion, erosion coefficient, power of erosion, density of dry sediment and erosion function. The bed layers can be soft and partly consolidated or dense and consolidated. Consolidation is included as a transition rate of sediment between the layers and liquefaction by waves is included as a weakening of the bed due to breakdown of the bed structure.
Explore related products
Let's get started
Complete this form and we will be in touch soon.



